IUCN/SSC Otter Specialist Group Bulletin

©IUCN/SCC Otter Specialist Group
Volume 36 Issue 1 (January 2019)
Citation: Raman, K, Sivangnanaboopathidossvimal, Kishorekumar, S, Krishnakumar, BM and Selvan, KM (2019). Occurrence of Smooth-Coated Otter Lutrogale perspicillata in Sankaraparani River, Puducherry, India. IUCN Otter Spec. Group Bull. 36 (1): 28 - 33
Occurrence of Smooth-Coated Otter Lutrogale perspicillata in Sankaraparani River, Puducherry, India
Kothandapani Raman1, Sivangnanaboopathidossvimal2, Sakthivel Kishorekumar3, Bawa M. Krishnakumar4 and Kanagaraj M. Selvan5
1 No:4/739, Dr, Ambedhkar Street, Kandamangalam (Post), Villupuram, Tamil Nadu, 605012
2 No:65, Second Cross Street, Kurunji Nagar Extension. Lawspet, Puducherry, 605008
3 No:24, Seventh Cross Street, Bharathinagar, Karauvadikuppam, Lawspet, Puducherry, 605008
4 Salim Ali School of Ecology & Environmental Science, Pondicherry University, R.V.Nagar,Kalapet, Puducherry 605014
5 5Scientist D/Joint Director, Project Elephant, Ministry of Environment Forest and Climate Change, Indhira Paryavaran Bhawan, New Delhi, 110003
e-mail: tamildove@gmail.com
Received 7th February 2018, accepted 30th December 2018
Abstract: Lack of robust data has so far impeded a proper appraisal on the distribution of any taxa. In this article, we present a record of smooth-coated Otter (Lutrogale perspicillata Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire, 1826) in the Sankaraparani River, Union territory of Puducherry, India, an area where it has previously not been recorded. As otters have been preying on fish entangled in fishing nets, fishermen have been killing them in retaliation, which is a significant conservation issue for the otter population
Keywords: Smooth-coated Otter, Sankaraparani River, Puducherry
INTRODUCTION
Data on distribution and ecology of many mesocarnivores are very limited. Three species of otters exist in India, of which smooth-coated Otter Lutrogale perspicillata is largest. Adapted for a semi-aquatic life, with webbed feet and a strong tapering tail that aids in propulsion (Johnsingh and Manjrekar, 2013). Smooth-coated Otters prey readily on fish, shrimp, crayfish, crab, insects, and vertebrates, such as frog, mudskippers, birds, and rats, form a significant part of their diet (Prater, 1971; Foster-Turley, 1992; Hussain and Choudhury, 1998). Geographically, the smooth-coated Otter ranges from Indonesia in South East Asia , to Pakistan in the West with an isolated population of this species (L. p. maxwelli) in the marshes of Iraq; this is the westernmost end of its distribution (Hussain, 1993). It has been classified under Schedule II of the Indian Wildlife (Protection) Act 1972 and categorized as a Vulnerable by IUCN Red list (De Silva et al., 2015), furthermore, it is listed in Appendix II of CITES. Herein we present a new site locality with a few incidental observations of smooth-coated Otters (SCO) from the Puducherry on Coromandel Coast of southern peninsular India.
Study Area
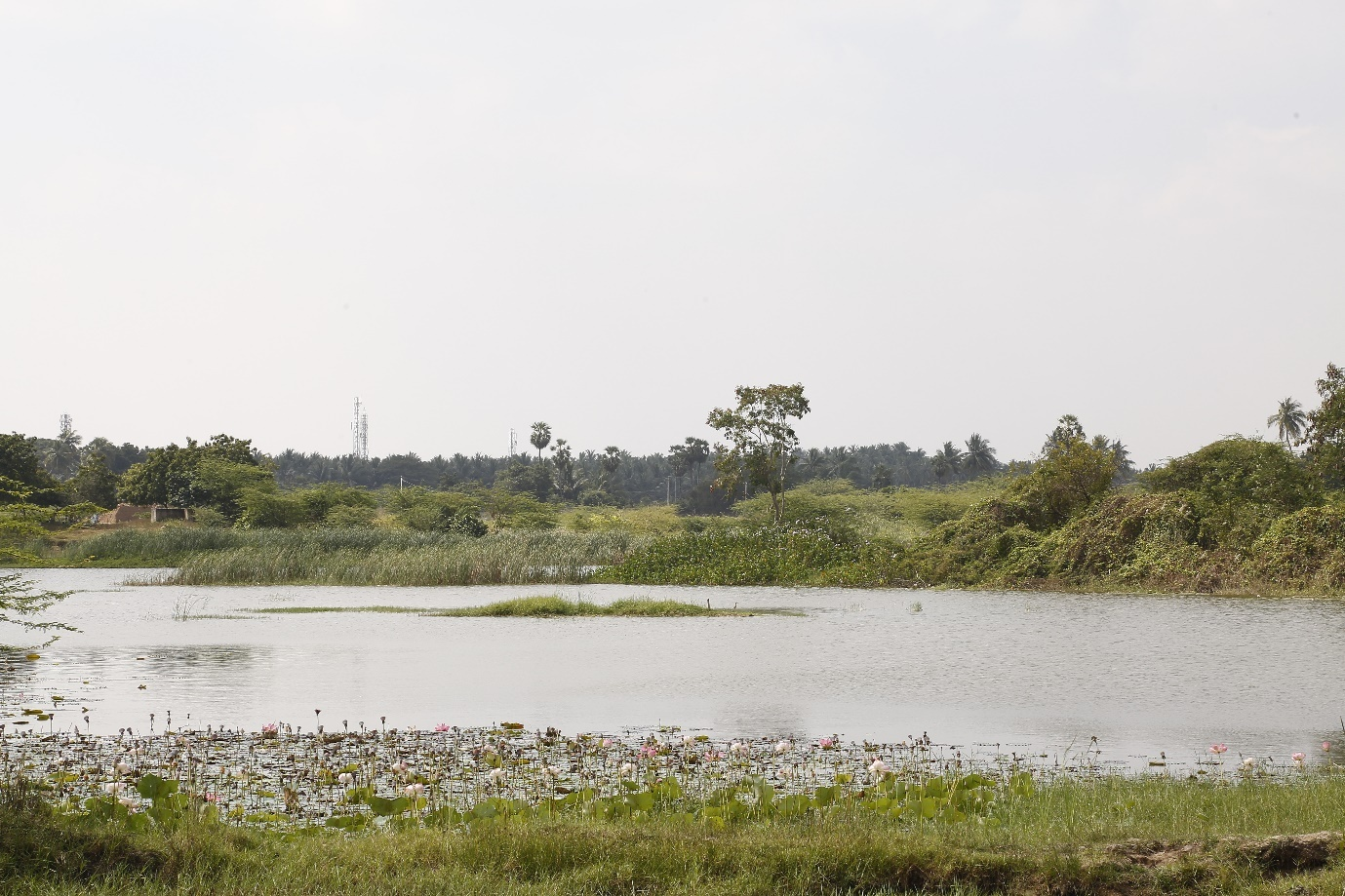
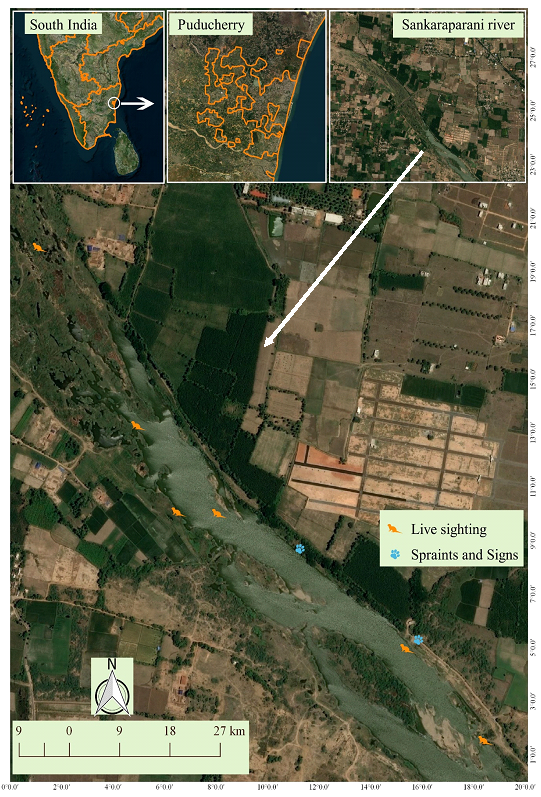
The Union territory of Puducherry (formerly known as Pondicherry) is located on the east coast of southern peninsular India. It consists of the districts of Karaikal, Yanam, and Mahe and Puducherry, the latter containing the capital; the union territories consist of adjacent collections of small enclave pockets in other states. One notable river in Puducherry originates on the western slope of Gingee hill in the Villupuram district of Tamil Nadu, and flows into the Bay of Bengal; it is known as the Sankaraparani river at Villianur in Puducherry district. Its ancient name was Varahanadi and Tondi (Figure 1). It splits off into separate branch at Ariyankuppam known as Chunnambaar (Vijayakumar et al., 2012). Bankside vegetation including Borassus flabellifer, Prosopis juliflora, Leucaena leucocephala, Morinda tinctoria, Albizia lebbeck, Bombex ceiba and Bambusa sp. grows along the bank of the river (Figure 2), and provides ideal refuge for SCO; it is also habitat for Golden Jackal (Canis aureus), Common grey mongoose (Herpestes edwardsii), Jungle cat (Felis chaus), common palm Civet (Paradoxurus hermaphroditus) and small Indian Civet (Viverricula indica).
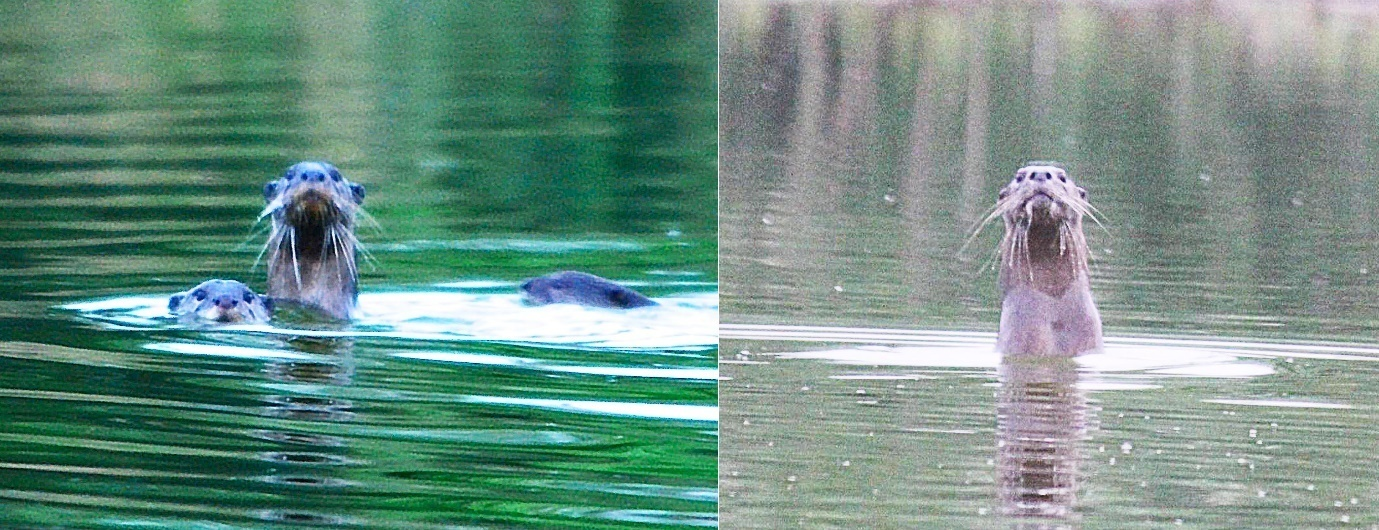
On 28th August 2017, we sighted a group of SCO including a pup while we were engaged on a bird survey. They were sinuously swimming parallel to the water flow (Figure 3).. Upon sighting us, they bounded into narrow-leaf cattail (Typha angustifolia), which is ubiquitous in the river. SCO have not been recorded previously in he Union territory of Puducherry. Ssince then, we have visited the location occasionally and made observations, which are summarized in Table 1.
| Table 1: Details of L. perspicillata records from Sankaraparani River. | ||||||
| Date of Visit | Number of Ind * | Time | Activity | GPS Location | ||
| 28.08.2017 | 3 | 1030 | Couple of SCO were swimming parallel to water flow. | N11°54’46.857” E79°’44’5.917” |
||
| 10.09.2017 | 1 | 1600 | Foraging till 1800 | N11°54’56.503” E79°43’51.92” |
||
| 01.10.2017 | 2 | 1500 to 1630 | Basking on a pile of sand that was covered with moss | N11°55’2.771” E79°43’45.911” |
||
| 22.10.2017 | 9 | 1830 | N11°54’56.613” E79°43’48.907” |
|||
| 05.11.2017 | Footprint | N11°54’40.307” E79°44’11.719” |
||||
| 26.11.2017 | 1 | 0600 | Rushed towards observer (who was swimming to photograph) and then emerged out of the water while looking at him for few minutes, possibly to investigate. | N11°54’46.85” E79°44’5.91” |
||
| 10.12.2017 | 2 | 0600 | Both were feeding on fish that was entangled in a fishing net | N11°54’47.5” E79°44’06.7” |
||
| 30.12.2017 | Foot-print & spraints | N11°54’54.0” E079°43’57.9” |
||||
| *Number of live individuals | ||||||
Threats
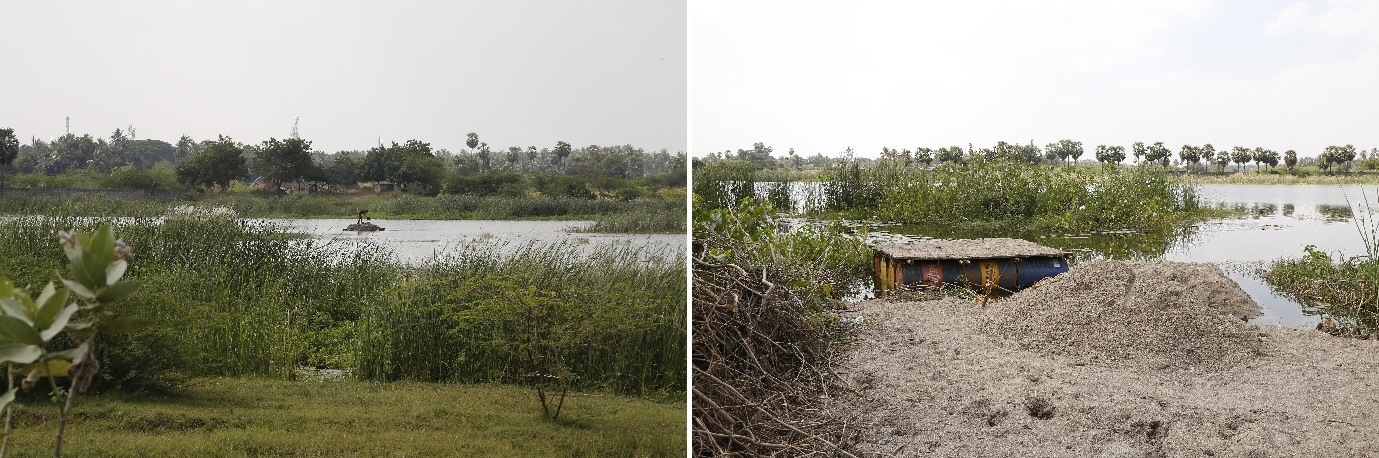
We interviewed a few residents and fishermen, who informed us that SCO have been depredating domestic fowl while they forage along the bank of the river and also catch and stealing the fish that are entangled in fishing nets. Because of this, fishermen have retaliated with the help of local hunters (Narikuravar). Also, indiscriminate sand mining in and along river bank destroy their habitat, holt being particularly vulnerable (Figure 4).
CONCLUSION
Retaliatory killing of SCO adversely affects the population locally. Strict implementation of the law for species conservation, and educating local residents and fishermen about the importance of this species in the ecosystem is crucial for this isolated remnant population. This initial observation provides an important baseline for further research and evaluation of conservation initiatives.
Acknowledgements: Authors are thankful to Mr. Iyappan and Mr. Sivashankaran for identifications of plants and Mr. Aravindh for photographs.
REFERENCES
De Silva, P., Khan, W.A., Kanchanasaka, B., Reza Lubis, I., Feeroz, M.M., Al-Sheikhly, O.F. (2015). Lutrogale perspicillata. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015.
Foster-Turley, P. (1992). Conservation ecology of sympatric Asian otters Aonyx cinerea and Lutra perspicillata. PhD thesis., University of Florida.
Johnsingh, A.J.T., Manjrekar, N. (2013). Mammals of South Asia, Vol. I. University Press, India.
Hussain, S.A. (1993). Aspects of the ecology of smooth-coated Otters Lutraperspicillata in National Chambal Sanctuary. Unpublished Ph.D Thesis. Center for Wildlife and Ornithology. Aligarh Muslim University. Aligarh, India.
Hussain, S.A., Choudhury, B.C. (1998). Feeding ecology of smooth-coated otter Lutraperspicillata in National Chambal Sanctuary. Proceedings of the Symposia of the Zoological Society of London. Behav. Ecol. Riparian Mamm. 71:229-250.
Prater, S.H. (1971). The book of Indian animals. 3rd edition. Mumbai: BNHS-OUP.
Vijaykumar, G., Sivasankaran, M.A., Murugaiyarn, V. (2012). Studies on the pollution levels in Ariyankuppam backwater, Puducherry region. Int. J. Sci. Environ. Technol. 1: 363-376.
Présence de la Loutre à Pelage Lisse Lutrogale pPerspicillata dans la Rivière Sankaraparani, à Puducherry, en Inde
Le manque de données fiables a jusqu'ici empêché une évaluation adéquate de la distribution de tous taxons. Dans cet article, nous présentons les données d’observation de loutre à pelage lisse (Lutrogale perspicillata Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire, 1826) dans la rivière Sankaraparani, territoire de l'Union de Puducherry, en Inde, une région où elle n'avait pas encore été répertoriée. Lorsque les loutres maraudent des poissons emmêlés dans des filets de pêche, les pêcheurs à la ligne les tuent en représaille, ce qui constitue un problème de conservation important pour la population existante.
Revenez au dessus
Resumen: Presencia de la Nutria Lisa Lutrogale perspicillata en el Río Sankaraparani, Puducherry, India
La falta de datos robustos impide una apreciación adecuada de la distribución de cualquier taxón. En este artículo, presentamos un registro de nutria lisa (Lutrogale perspicillata Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire, 1826) en el río Sankaraparani, territorio de Puducherry, India, un área en la cual no había anteriormente registrada. Como la nutria merodea alrededor de los peces enredados en las redes de pesca, los pescadores las han venido matando en forma retaliatoria, lo que es un significativo problema de conservación para la población existente
Vuelva a la tapa